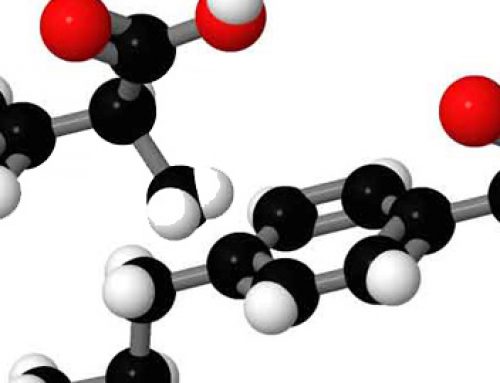
Anthocyanins are a class of chemicals found in the leaves, stems, flowers & fruits of a variety of plants. These include cherries, blueberries, cranberries and blackberries.
The role such chemicals play in plants is quite varied. One of the most important roles is of course reproduction. Brightly colored flowers attract pollinators such as bees & humming birds while colored fruits signal food sources. This in turn contributes to seed dispersion.
Primates such as humans, apes & monkeys are unique among mammals in having superior color vision. The evolution of this trait may in part be related to being able to find fruit among all the green leaves.
Anthocyanin-A Natural Sunscreen?
Beyond their function in plant reproduction, the anthocyanins have other interesting characteristics. If you look at the chemical structure, you can see that it has many double bonds much like melanin which our skin produces in response to UV photons in sunlight.

Anthocyanin is a plant pigment found in cherries. Note the extensive double bonds similar to melanin & sunscreens such as PABA. This is believed to also protect the plant from damage due to strong sunlight, particularly UV.
Anthocyanin-A pH Indicator?
Anthocyanin also appears to be a type of pH litmus indicator molecule turning pink in acidic solutions (<ph 7), purple in neutral solutions (pH 7) greenish yellow in basic solutions (>pH 7) & colorless in very alkaline liquids (~pH 13).

Litmus paper changes color reversibly in response to acids & bases. The reaction is reversible in anthocyanins as well.
(Image courtesy of: science7acidbase.wikispaces.com/Litmus+Paper)
Anthocyanins-Potential Solar Cells?
The double bonds which allow anthocyanin to act as a sunscreen may also make it useful as an organic solar cell material. The chemical has been shown to convert the energy of light photons into electricity.
Anthocyanin-An Antioxidant?
Although there is some indication that the anthocyanin molecule may have some antioxidant activity, it may not be significant. The real advantage in eating a bowl of cherries may simply be that it is NOT a fat or salt laden meal of hamburger & french fries.