Pesticides refer to both insecticides and herbicides that kill unwanted insects or plants, respectively. They work by disrupting chemical pathways in important metabolic processes. Safe handling & avoidance of repeated high doses is best practice.
Note: We sold our original domain indigo.com in January 2018. Ignore the reference to it in the images. We now use www.indigoinstruments.com.
How Does Permethrin Work?
Permethrin is an insecticide derived from compounds similar to those found naturally in chrysanthemums. Mosquitoes and head lice are among the principal targets of permethrin which acts as a neurotoxin. Permethrin attacks the host’s nervous system by binding to sodium ion channels. One effect of this is an uncontrolled increase in the insect’s body temperature. Warm-blooded organisms such mammals are less susceptible. Our livers readily break down permethrin & excrete the resulting metabolites.
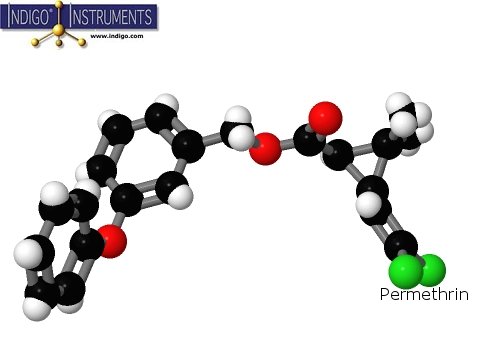
Permethrin is similar to compounds found in chrysanthemums.
How Does Glyphosate Work?
Glyphosate is a herbicide designed to prevent the growth of weeds that compete with cultivated crops such as corn, soy, canola, and cotton. It is otherwise a broad-spectrum chemical that can kill other plants such as lawn grass and desirable garden plants. It targets plant enzymes involved in the production of several amino acids. It is most effective when applied while the weeds are actively growing.
These enzymes are specific to plant pathways and should not target amino acid metabolism in humans and other animals. Some health authorities however have suggested glyphosate may not be completely safe. Handle with caution.
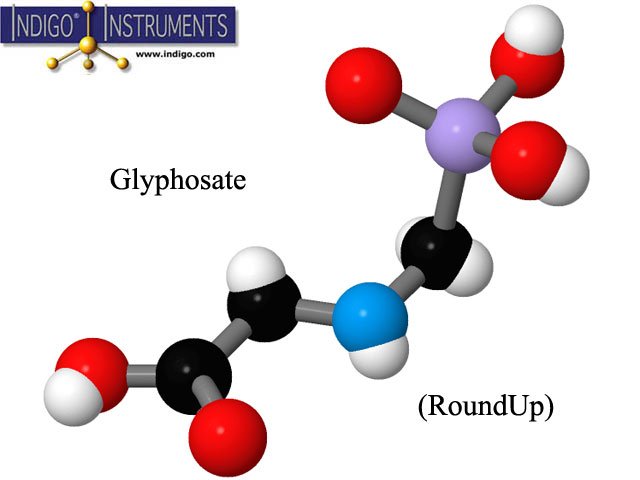
Glyphosate, aka Roundup, interferes with amino acid production in plants.
How Does Malathion Work?
Malathion is an insecticide that has been used to combat a variety of pests ranging from fruit flies to mosquitoes. It acts on an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase which mediates the effects of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine regulates muscle activity under the control of the nervous system.
Malathion is a potent neurotoxin, similar in action to nerve gases such as Sarin. Humans share many of the acetylcholiene biochemical pathways with insects and other invertebrates & vertebrates so handle this chemical with great caution.
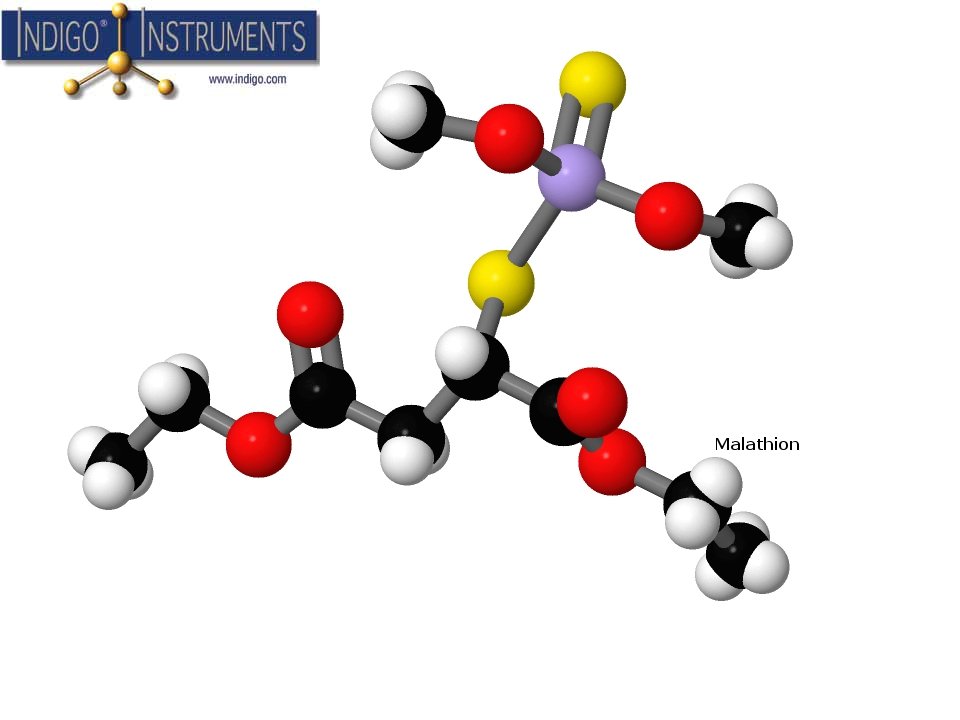
How Does DDT Work?
At one time DDT was a valuable pesticide in the control of mosquitoes that carried dangerous diseases such as malaria and typhus. It acted by causing uncontrolled firing of nerve impulses that resulted in muscle spasms that eventually led to death.
While not very toxic to humans, DDT is concentrated in the food chain & is particularly harmful to top predators such as eagles, condors, and falcons. DDT caused the thinning of bird eggshells which in turn increased mortality in their offspring. For this reason, various health authorities around the world banned DDT usage in the 1980s.
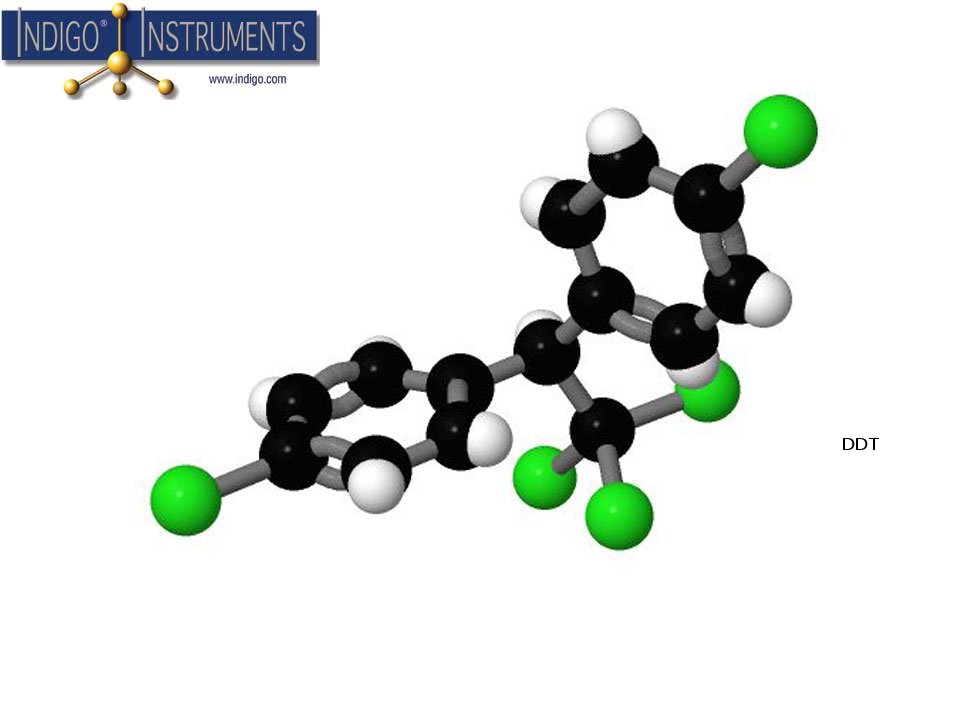
DDT was important to malaria control but had adverse effects on top-level avian predators.
Conclusion
Pesticides are a convenience that we would find hard to live without. While safe if used occasionally & according to instructions, caution should still be taken. Don’t handle concentrates without gloves & respirators. If you do get them on your skin, wash them off with soap. Do not make a habit of spraying upwind.
References
-
- Wikipedia. See: DDT Mechanism of Action




